- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
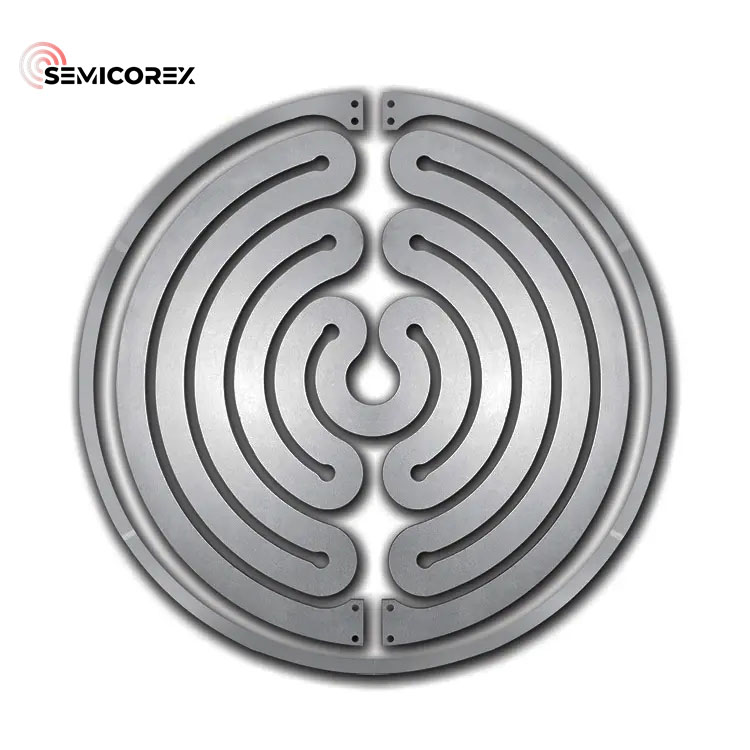
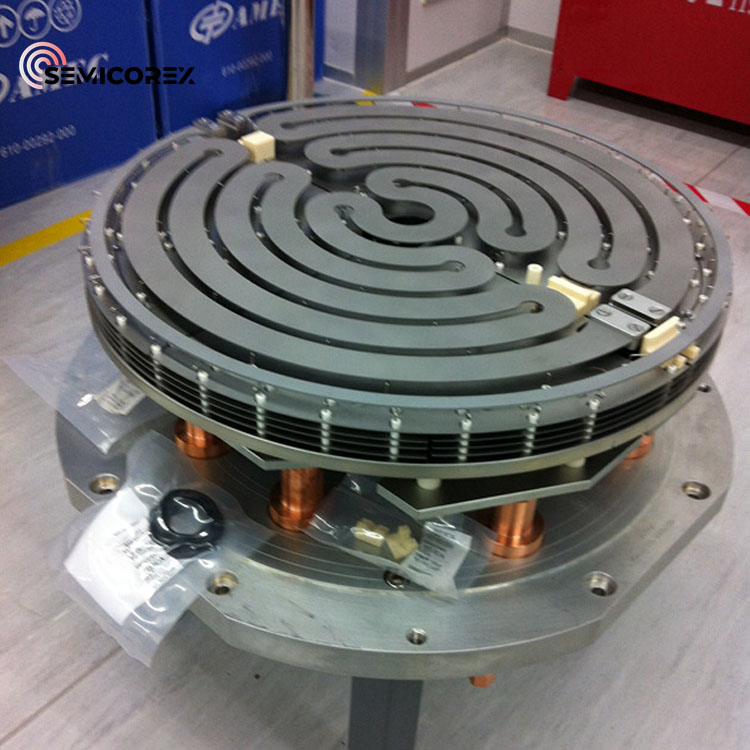
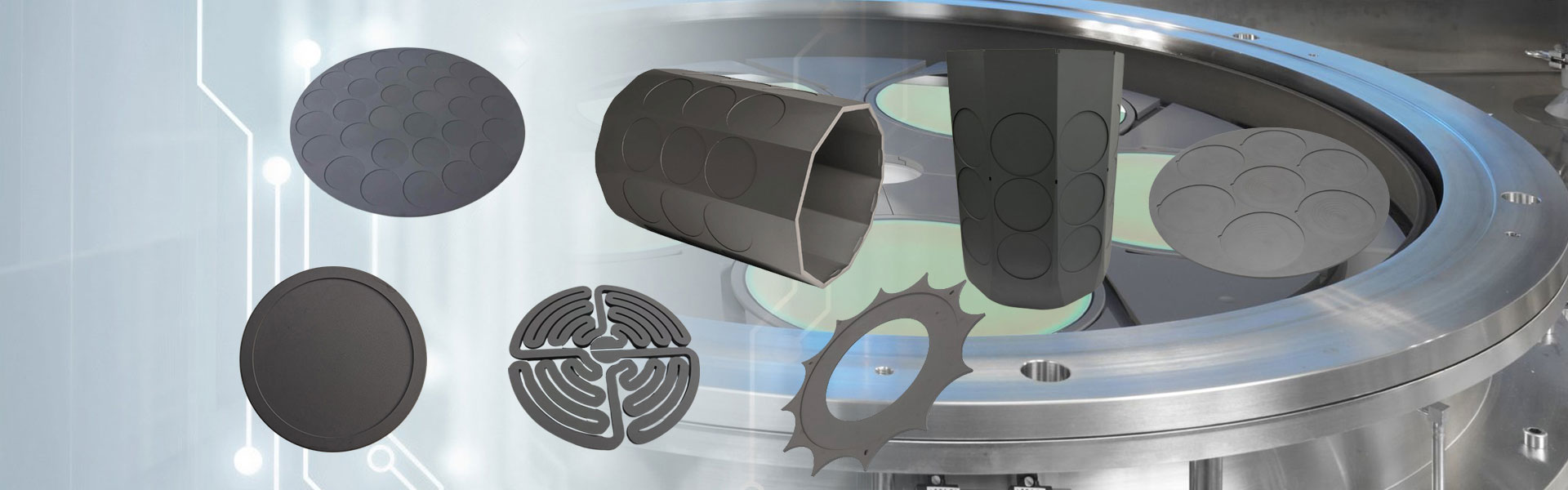
SiC Steering Mirror
Semicorex SiC Steering Mirror is a remarkable material that combines durability, resilience, and exceptional optical performance, making it indispensable in advanced optical systems across various high-tech industries.
Send Inquiry
Semicorex SiC Steering Mirror Material Properties
Outstanding Material Characteristics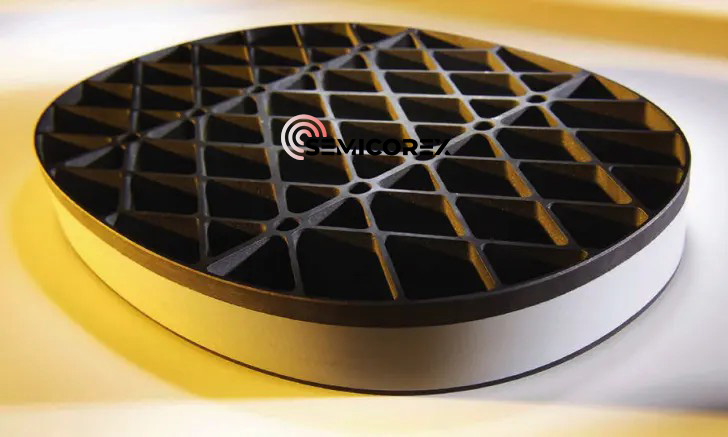
Because of its exceptional material qualities, the SiC Steering Mirror is the material of choice for satellite mirrors in telescopes. Silicon carbide (SiC) is renowned for its exceptional resistance to deformation due to its high stiffness and hardness. This is essential for preserving optical accuracy in difficult settings. Because of its low density, the structure is lightweight, which is especially useful in aeronautical applications where every gramme matters. Additionally, SiC's low coefficient of thermal expansion reduces dimensions changes under temperature fluctuations, preserving optical alignment and performance, while its excellent thermal conductivity guarantees effective heat dissipation.
Mechanical and Thermal Resilience
The SiC steering mirror can resist temperatures of up to 1400°C, demonstrating exceptional thermal stability. Applications requiring quick temperature changes, such space telescopes and high-speed scanning systems, depend on this feature. The flexural strength of the material, which ranges from 59,465 to 93,549 PSI, highlights its capacity to withstand mechanical pressures without sacrificing structural integrity. SiC can be brittle despite its mechanical strength, therefore treating it carefully during production and installation is necessary to avoid damage.
Lightweight Design and Surface Quality
Reduced roughness on the SiC steering mirror's surface contributes to its excellent optical performance and reduced light scatter. For applications like high-energy laser (HEL) systems that need precise light manipulation, this is essential. SiC is also substantially lighter than conventional glass mirrors, which is an important characteristic for space applications and big telescopes where weight reduction is critical. In addition to making handling and installation simpler, this lightweight design lowers the total payload for aeronautical missions.
Frequency of Resonance and Stiffness
SiC Steering Mirror is perfect for applications involving acceleration, like HEL systems, because it has resonant frequency advantages over materials like Zerodur. High acceleration and quick passive heat dissipation are made possible by its remarkable rigidity, which is essential for sustaining performance in dynamic settings. SiC's adaptability is further increased by its capacity to be formed into intricate shapes, which enables the creation of unique patterns that are suited to particular optical needs.
CVD Coating Enhancements
Chemical vapour deposition (CVD) is used to improve the SiC steering mirror's surface properties. By achieving a superior surface figure, CVD SiC can enhance optical quality. Additionally, the CVD cladding process enhances the mirror's overall performance and longevity, guaranteeing that it satisfies the exacting requirements of sophisticated optical systems.

Uses for SiC Steering Mirrors
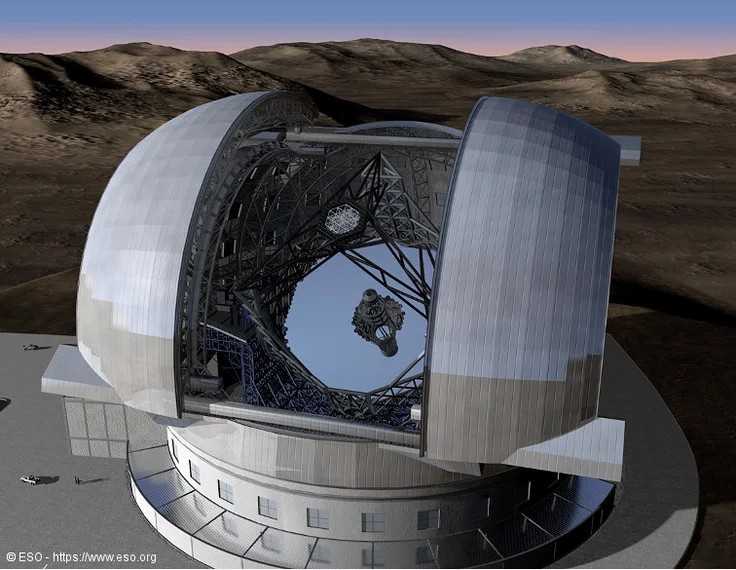 Applications in Space and Aerospace
Applications in Space and Aerospace
SiC Steering Mirror's lightweight and thermally stable qualities make it perfect for space and aerospace applications. The capacity of the mirror in satellite telescopes to preserve optical accuracy in harsh space environments guarantees dependable operation during long missions. In the zero-gravity environment of space, where maintaining alignment is essential for precise data collecting, its resistance to dynamic and gravitational deflection is very advantageous.
Fast Scanning Mechanisms
The SiC Steering Mirror's mechanical robustness and quick thermal stabilisation allow for precise control and fast reaction times in high-speed scanning systems. These systems gain from the mirror's capacity to tolerate rapid acceleration and effectively dissipate heat, guaranteeing steady performance even in the face of severe operating circumstances.
Applications of High Energy Lasers (HEL)
The SiC Steering Mirror's remarkable rigidity and resonant frequency advantages are priceless for HEL applications. The mirror is a perfect part of laser systems that need accurate beam control and stability because of its capacity to withstand large energy loads and quickly dissipate heat. Its capacity to take on intricate shapes enables customised solutions that satisfy the unique requirements of cutting-edge laser technology.
Big Telescopes
The SiC Steering Mirror's low scatter surfaces and lightweight design improve optical performance in large telescopes. In addition to making installation and alignment simpler, the lighter weight permits greater mirror diameters without sacrificing structural integrity. In astronomical applications, where observing far-off celestial objects requires optimising light gathering, this is significant.
SiC Manufacturing Process
SiC is produced via a number of complex procedures. First, silica sand or liquid silicon is heated with carbon in a high-temperature furnace to create silicon carbide. Through this technique, dense SiC is created, which is subsequently sintered under high pressure and in an inert atmosphere at temperatures above 2000°C with non-oxide sintering additives. Furthermore, highly pure SiC is produced in a face-centered cubic crystal form via chemical vapour deposition, improving its mechanical and optical characteristics.