- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
Industry News
What is the Difference Between Graphitization and Carbonization
In conclusion, both graphitization and carbonization are industrial processes that involve carbon either as a reactant or a product. Carbonization refers to the process of converting organic matter into carbon, while graphitization involves transforming carbon into graphite. Therefore, carbonization......
Read MoreSemiconductor doping process
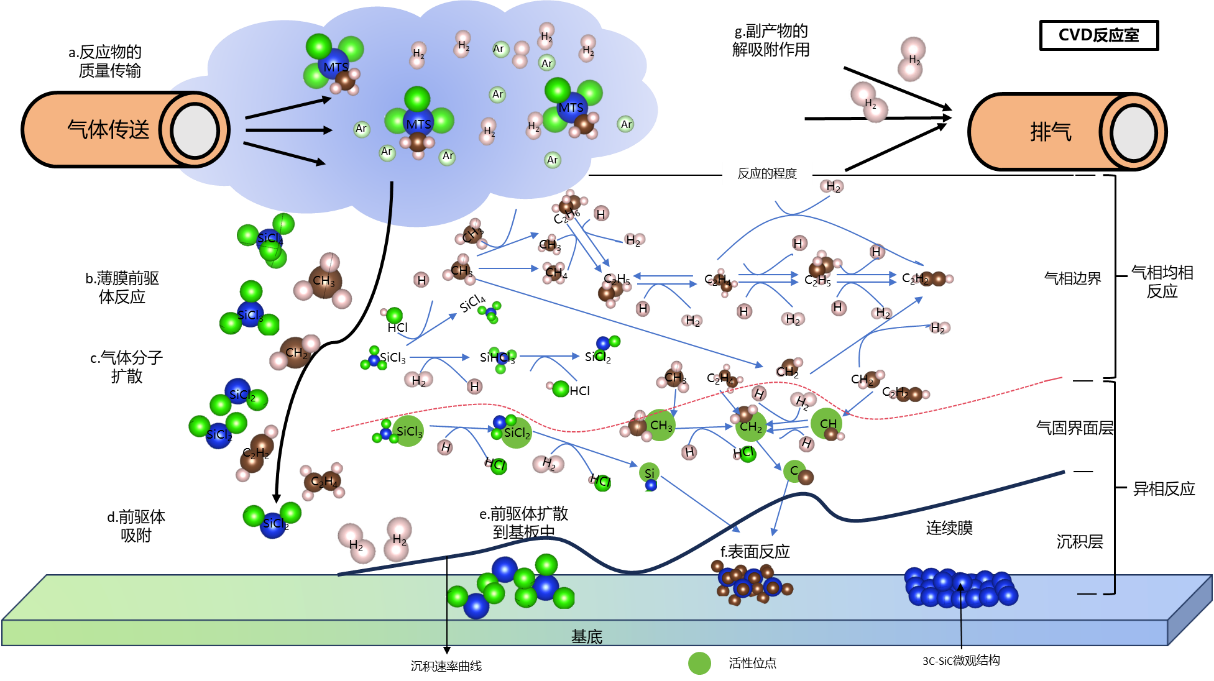
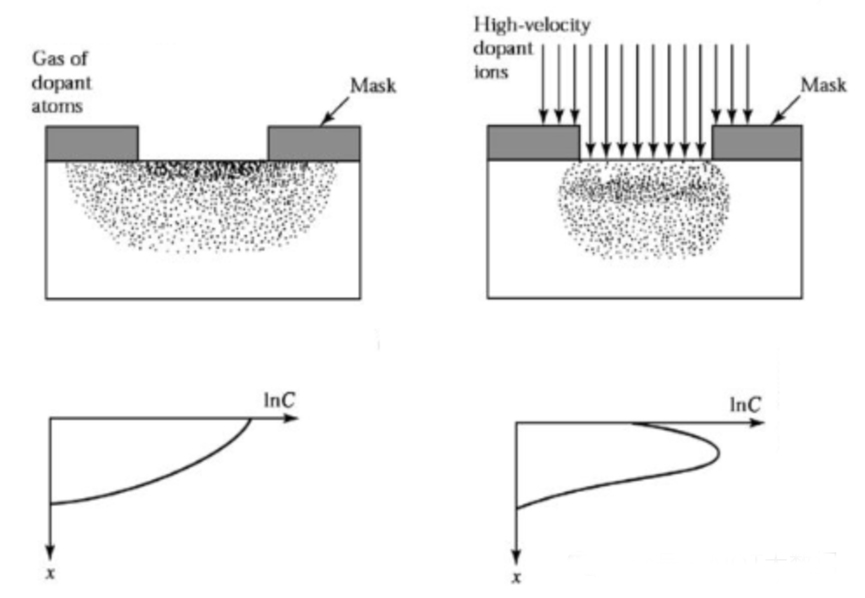
One of the unique properties of semiconductor materials is that their conductivity, as well as their conductivity type (N-type or P-type), can be created and controlled through a process called doping. This involves introducing specialized impurities, known as dopants, into the material to form junc......
Read More