- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
Laboratory Glassware
Semicorex Laboratory Glassware is mainly made of high-quality quartz material, it is a material known as high quality and thermal resistance, while the cost is relatively low. Semicorex provide the qualified products based on customers’ needs.*
Send Inquiry
Semicorex quartz Laboratory Glassware is commonly in the lab. Quartz glass is well-known as extremely high quality and excellent thermal resistance properties. It can stand the high temperature and not be deformation, also it has a great optics properties, so that the quartz glass is the ideal choice in some high purity and thermal resistance fields, such as semiconductor processing and scientific research field.
Quartz glass has a melting point of 1750°C and can be used continuously at temperatures up to 1100°C. It is resistant to thermal shock and does not easily crack when subjected to rapid heating and cooling. A quartz glass test tube that has just been sintered with an oxy-hydrogen flame will not easily shatter even if immediately placed in cold water. Furthermore, compared to other types of glass, Laboratory Glassware made by quartz glass has better resistance to acids and alkalis.
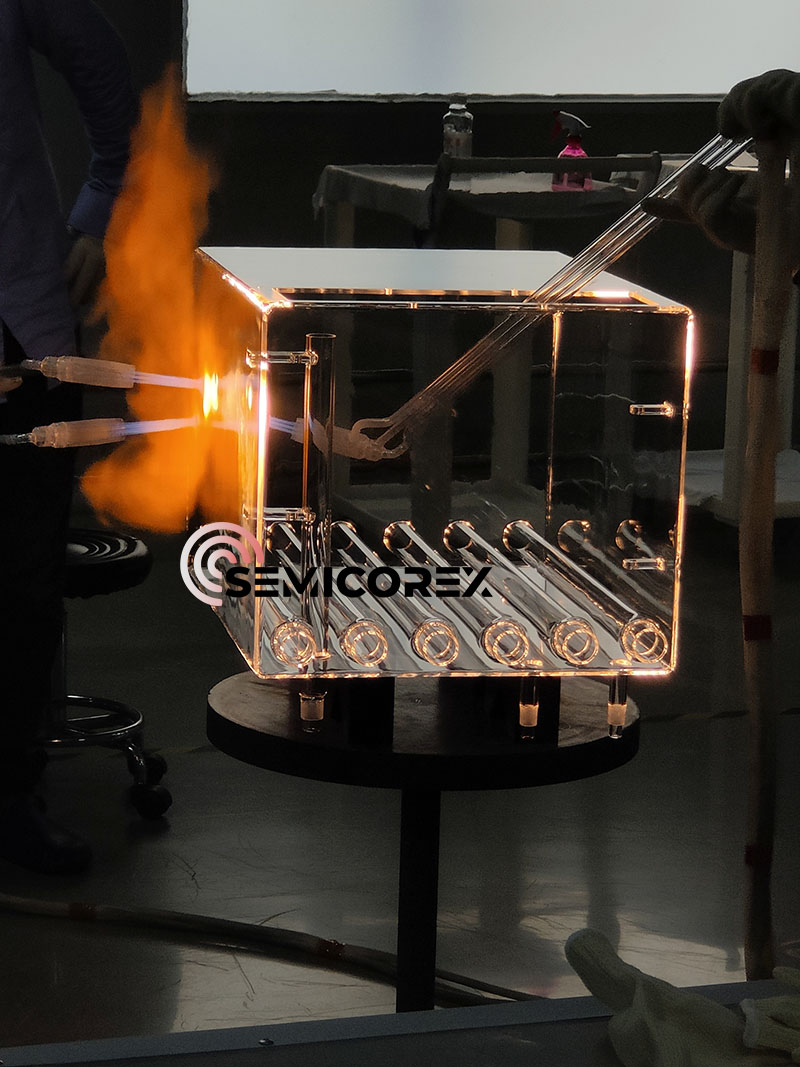
Quartz glass is frequently used in laboratory high-temperature experiments, optical experiments, chemical experiments, vacuum experiments, analytical instrument components, and some special experimental environments, specifically as follows: 1. High-temperature reactions, sample calcination, and melting experiments often utilize quartz glass beakers, crucibles, quartz furnace tubes, quartz boats, and quartz reaction tubes; 2. Optical applications mainly include UV windows, prisms, lenses, cuvettes, and laser protective mirrors; 3. In chemical experiments, quartz containers are commonly used to hold highly corrosive solutions (acidic solutions other than hydrofluoric acid), and quartz distillation apparatus is used in the preparation of high-purity chemical reagents; 4. Quartz glass can also be used for vacuum coating equipment windows, electron microscopes, and high-temperature furnace windows requiring high temperature resistance and a vacuum environment; 5. Quartz capillaries are used in pigment analyzers, quartz torch tubes are used in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, and quartz components are also used in the burner heads of atomic absorption spectrometers; in addition, quartz glass is also used in some special environments such as radiation environments, low-temperature environments, and light-induced corrosion environments, including quartz plates, liquid nitrogen cups, and microfluidic chips.
Laboratory glassware forms the foundation of science because of its importance in today’s research. Laboratory glassware is used extensively for experiments related to chemistry, biology, materials science, environmental studies, and analytical testing. The properties of quartz glassware allow laboratories to have precision, safety, and reliability.
One of the greatest advantages of quartz glassware is that researchers can have a consistent and accurate result. Therefore, the quality of the quartz glassware used in laboratories directly affects the success and reproducibility of any experiment conducted by a researcher, as well as the advancement of the field in which they work. Today, the use of high-quality quartz components is a necessity in nearly all areas of advanced scientific investigation.
The physical and chemical properties of quartz laboratory glassware with several unique attributes. Quartz is made from highly pure fused silica, allowing quartz to possess properties that enable it to withstand rapid temperature fluctuations during experiments without cracking or deforming. This property is particularly useful in laboratories that conduct routine high-temperature, heating, or cooling experiments.
Quartz has a low thermal expansion coefficient compared to the glass most commonly used in laboratories (borosilicate glass). This property of quartz allows for dimensional stability even when subjected to extreme heat or thermal cycles. Therefore, when researchers perform extreme heat and thermal cycle tests, quartz glassware is much more reliable than borosilicate glassware.
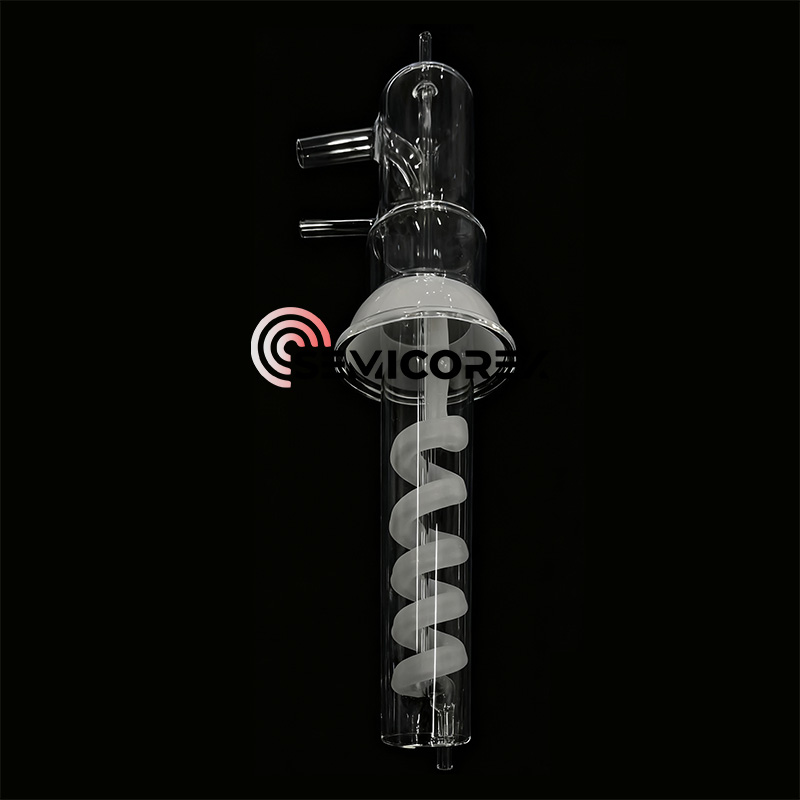
The range of quartz glassware used in laboratories is vast, covering both standard apparatus and highly specialized components. Beakers, flasks, test tubes, crucibles, cuvettes, condensers, and reaction vessels are just some examples of the many types of laboratory glassware available for use in laboratories today. The primary purpose of laboratory glassware is to withstand extreme temperatures and fluids' harsh environments.
More advanced laboratories may require specialised quartz products. Examples of such products include multi-neck flasks for distillation, quartz tubes for use in a furnace, flow cells for spectroscopy, microreactors for use in controlled chemical synthesis, and evaporation dishes for processing high-temperature materials. Because quartz can be manufactured, moulded, and polished with a high degree of accuracy, it makes an ideal material for producing any component that needs to meet tight tolerances for either dimensional accuracy or optical quality. Researchers will see consistent performance, long service life, and very little maintenance, even when using quartz glassware repeatedly in extreme environments.
With the increased sophistication of scientific research, laboratories are more reliant upon reliable, contamination-free, equipment designed to deliver accurate, repeatable results than ever before. Quartz glassware provides the ideal solution for laboratories in terms of durability, purity, and performance; with respect to operating safety and the potential for the maximum amount of accurate measurements. Because quartz components last longer than traditional laboratory-grade glasses under extremely severe conditions, they are also the most economical choice.