- English
- Español
- Português
- русский
- Français
- 日本語
- Deutsch
- tiếng Việt
- Italiano
- Nederlands
- ภาษาไทย
- Polski
- 한국어
- Svenska
- magyar
- Malay
- বাংলা ভাষার
- Dansk
- Suomi
- हिन्दी
- Pilipino
- Türkçe
- Gaeilge
- العربية
- Indonesia
- Norsk
- تمل
- český
- ελληνικά
- український
- Javanese
- فارسی
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- नेपाली
- Burmese
- български
- ລາວ
- Latine
- Қазақша
- Euskal
- Azərbaycan
- Slovenský jazyk
- Македонски
- Lietuvos
- Eesti Keel
- Română
- Slovenski
- मराठी
- Srpski језик
Ceramic Heaters
2025-04-16
In the front-end process (FEOL) of semiconductor manufacturing, the wafer needs to be subjected to various process treatments, especially the wafer needs to be heated to a certain temperature, and there are strict requirements, because the uniformity of temperature has a very important impact on the product yield; at the same time, semiconductor equipment needs to work in the presence of vacuum, plasma and chemical gases, which requires the use of ceramic heaters. Ceramic heaters are important components of semiconductor thin film deposition equipment. They are used in the process chamber and directly contact the wafer to carry and enable the wafer to obtain a stable and uniform process temperature and to react with high precision on the surface of the wafer to generate thin films.
Because the thin film deposition equipment used by ceramic heaters involves high temperatures, ceramic materials mainly based on aluminum nitride (AlN) are generally used. Because aluminum nitride has electrical insulation and excellent thermal conductivity; in addition, its thermal expansion coefficient is close to that of silicon, and it has excellent plasma resistance, it is very suitable for use as a semiconductor equipment component.
Electrostatic chucks (ESCs) are mainly used in etching equipment, mainly aluminum oxide (Al2O3). Since the electrostatic chuck itself also contains a heater, taking dry etching as an example, it is necessary to control the wafer at a specific temperature in the range of -70℃~100℃ to maintain a certain etching characteristic. Therefore, the wafer needs to be heated or dissipated by the electrostatic chuck to accurately control the wafer temperature. In addition, in order to ensure the uniformity of the wafer surface, the electrostatic chuck often needs to increase the temperature control zone to control the temperature of each temperature control zone separately to improve the process yield. Of course, with the development of technology, the distinction between traditional ceramic heaters and electrostatic chucks has begun to become blurred. Some ceramic heaters have the dual functions of high-temperature heating and electrostatic adsorption.
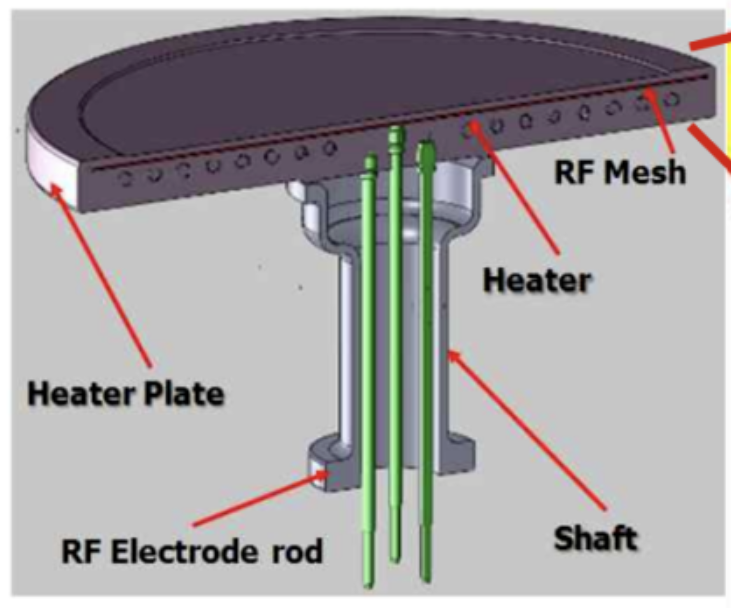
The ceramic heater includes a ceramic base that carries the wafer and a cylindrical support body that supports it on the back. Inside or on the surface of the ceramic base, in addition to the resistance element (heating layer) for heating, there is also a radio frequency electrode (radio frequency layer). In order to achieve rapid heating and cooling, the thickness of the ceramic base should be thin, but too thin will also reduce the rigidity. The support body of the heater is generally made of a material with a thermal expansion coefficient similar to that of the base, so the support body is often also made of aluminum nitride. The heater adopts a unique structure of a shaft (Shaft) joint at the bottom, which can protect the terminals and wires from the effects of plasma and corrosive chemical gases. A heat conduction gas inlet and outlet pipe is provided in the support body to ensure uniform temperature of the heater. The base and the support body are chemically bonded with a bonding layer.
Semicorex offers high-quality ceramic heaters. If you have any inquiries or need additional details, please don't hesitate to get in touch with us.
Contact phone # +86-13567891907
Email: sales@semicorex.com




